Created by - Anil Chauhan
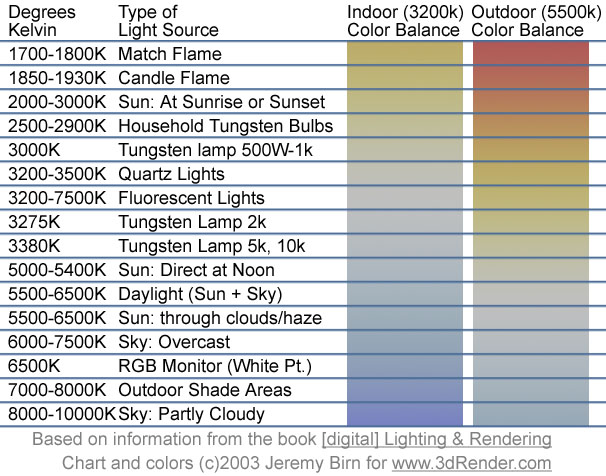
VRay lights
VRay lights are part of the VRay rendering engine, which is a popular software used for creating realistic computer-generated images and animations. VRay provides advanced rendering capabilities and is widely used in industries such as architecture, design, and entertainment. In the context of VRay lights, these are tools that allow you to simulate and control various lighting conditions in a virtual scene. Proper lighting is crucial for creating realistic and visually appealing renderings. VRay offers several types of lights that users can utilize to achieve different lighting effects. Here are some common VRay light types: 1. VRay Dome Light: This light type is often used to simulate global illumination and environmental lighting. It's commonly used for creating realistic outdoor scenes or providing ambient lighting. 2. VRay Sun and Sky: These lights work together to simulate the sun and sky in outdoor scenes. The VRay Sun is used to simulate direct sunlight, while the VRay Sky is responsible for the ambient lighting from the sky. 3. VRay Rectangle Light: This is a versatile light source that can be shaped and positioned as needed. It's often used for area lighting and can simulate lights such as fluorescent tubes or LED panels. 4. VRay IES Light: IES (Illuminating Engineering Society) lights allow users to use real-world photometric data for light distribution. This can be useful for accurately simulating the characteristics of specific light fixtures. 5. VRay Spotlight: This is a directional light source that can be focused on a specific area. It's often used for creating spotlight effects. Each type of VRay light comes with various parameters and settings that allow users to control the intensity, color, and other properties of the light. VRay lights play a crucial role in achieving realistic lighting in virtual scenes and contribute significantly to the final quality of rendered images.
More detailsPublished - Tue, 19 Dec 2023

Created by - Anil Chauhan
Materials in Unreal Engine
Certainly! Materials in Unreal Engine play a crucial role in defining the appearance of surfaces and objects in a virtual environment. They are a combination of textures, shaders, and other settings that determine how light interacts with a surface. Here's an overview of Unreal Engine materials:1. **Material Editor:** - Unreal Engine provides a node-based Material Editor that allows artists and developers to create complex materials visually. It uses a graph-based system where nodes represent different operations and functions.2. **Basic Components of a Material:** - **Textures:** These are 2D images that are applied to surfaces to simulate different properties like color, roughness, metallic, normal maps, and more. - **Scalars and Vectors:** Values used to control various properties of the material, such as color, roughness, metallicness, etc. - **Mathematical Operations:** Nodes for performing operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and more on scalar or vector values. - **Functions and Shaders:** Specialized nodes for controlling complex visual effects, such as fresnel effects, displacement, and custom shaders.3. **Physically Based Rendering (PBR):** - Unreal Engine uses a PBR approach to materials, which means that materials are designed to simulate real-world lighting and shading conditions. This includes properties like albedo (base color), metalness, roughness, and normal maps.4. **Material Instances:** - Material Instances allow for the creation of variations of a base material without duplicating the entire material. They can be adjusted in real-time to achieve different looks or respond to dynamic changes in the game.5. **Material Functions:** - Material Functions are reusable, self-contained graphs that can be embedded within other materials. They are useful for creating modular and easily maintainable material setups.6. **Dynamic Material Instances:** - Unreal Engine allows for the creation of Dynamic Material Instances that can be modified at runtime. This enables dynamic changes to materials during gameplay, such as color changes, emissive effects, or texture swapping.7. **Material Expressions:** - Material Expressions are nodes within the Material Editor that perform specific functions, such as texture sampling, normal map operations, or mathematical computations.8. **Material Parameters:** - Parameters in materials are exposed properties that can be adjusted externally, allowing for easy customization of materials in different instances or variations.9. **Material Layers and Blend Modes:** - Unreal Engine supports material layering, allowing the stacking of multiple materials with different blend modes to achieve complex visual effects. This is particularly useful for creating realistic surfaces with multiple layers, such as dirt on top of a base material.Understanding how to create and manipulate materials is essential for achieving realistic and visually appealing graphics in Unreal Engine projects. Artists and developers often spend significant time refining materials to achieve the desired look and feel for their virtual environments.
More detailsPublished - Wed, 20 Dec 2023
Created by - Anil Chauhan
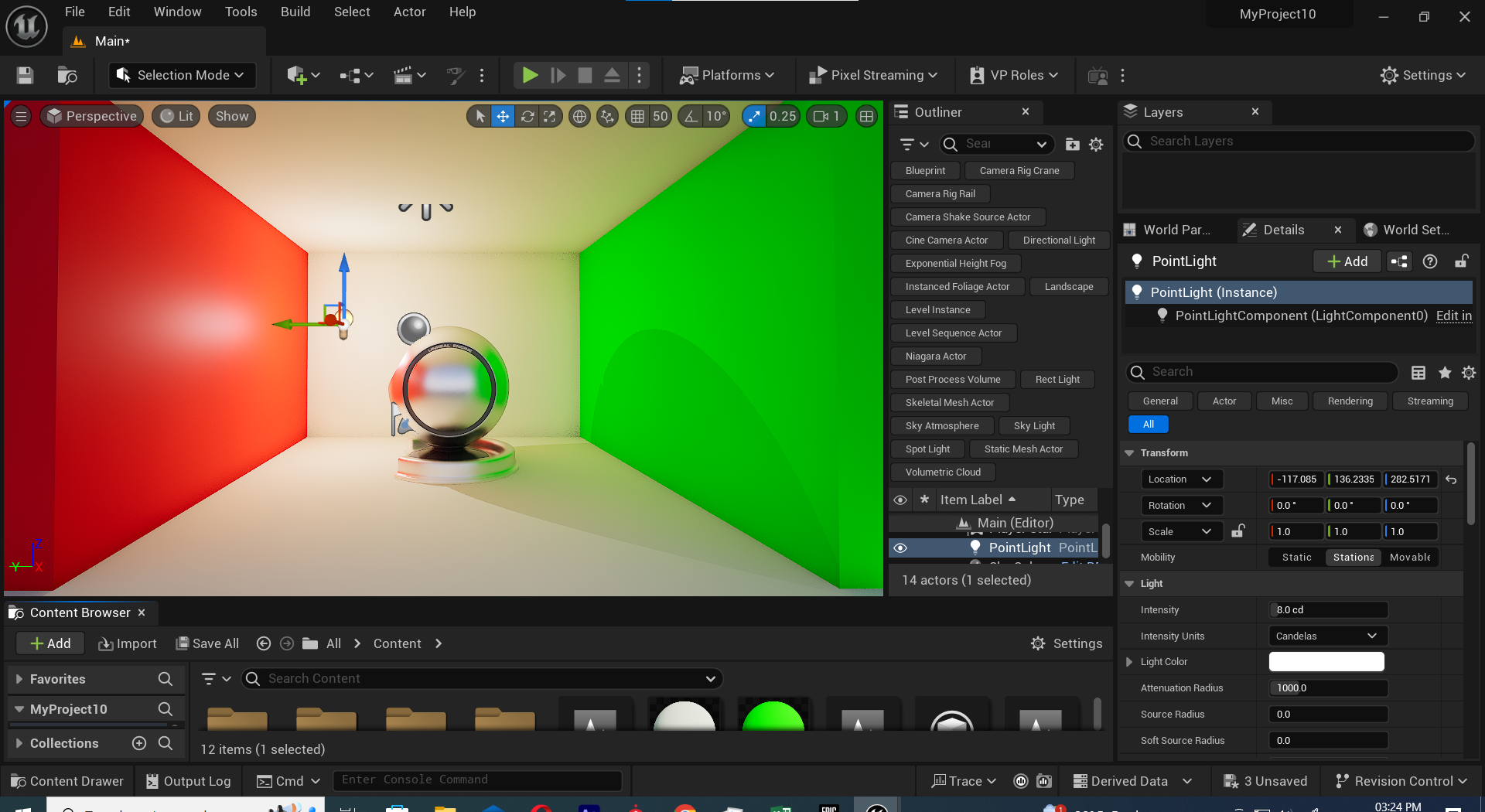
lights in Unreal Engine
an overview of lights in Unreal Engine. Unreal Engine is a popular game development engine, and it offers a sophisticated lighting system to create realistic and immersive visuals in games and other virtual experiences. Here are some key aspects of lights in Unreal Engine:1. **Types of Lights:** - **Point Light:** A light source that emits light in all directions from a single point in 3D space. - **Spotlight:** A directional light with a cone-shaped emission, simulating a focused light beam. - **Directional Light:** A light source that emits parallel light rays in a specific direction, often used to simulate sunlight.2. **Properties and Settings:** - **Intensity:** Controls the brightness of the light. - **Color:** Determines the color of the light emitted. - **Attenuation:** Defines how the light diminishes with distance. - **Radius/Length:** Specifies the reach or size of the light source. - **Cone Angle/Exponent (Spotlight):** Defines the cone angle and falloff for spotlight.3. **Lighting Effects:** - **Dynamic Shadows:** Unreal Engine supports dynamic shadow casting from lights, providing realistic shadow effects that change in real-time based on the position of the light source and the objects in the scene. - **Light Functions:** These are textures that can be used to modulate the light's color and intensity, allowing for advanced effects like animated lights or complex patterns.4. **Global Illumination and Reflections:** - Unreal Engine also supports advanced features like Global Illumination (GI) and Reflections. GI simulates indirect lighting, making scenes more realistic, while reflections create accurate reflections of objects in shiny surfaces.5. **Lighting Scenarios:** - Unreal Engine allows developers to set up different lighting scenarios for various times of day or environmental conditions. This can be achieved through dynamic day-night cycles or manual adjustments.6. **Lighting Quality:** - Unreal Engine provides scalable settings for lighting quality, allowing developers to balance visual fidelity with performance based on the target platform.7. **Lighting in Sequencer:** - Unreal Engine's Sequencer tool allows for cinematic storytelling, and it includes features for controlling lights in animated sequences.Understanding and effectively using lights in Unreal Engine is crucial for achieving visually stunning and immersive environments in games or other interactive experiences. Developers often spend considerable time fine-tuning lighting to achieve the desired atmosphere and realism in their projects.
More detailsPublished - Wed, 20 Dec 2023
Created by - Anil Chauhan
Adobe After Effects 2024 24.1.0.78
Adobe After Effects is a powerful motion graphics and visual effects software widely used in the film, television, and web design industries. If you're just getting started with After Effects, here's a step-by-step guide to help you familiarize yourself with the basics:### 1. **Installation:** - Make sure you have Adobe After Effects installed on your computer. You can get it through Adobe Creative Cloud.Overview of Adobe After Effects CC BenefitsCreate animated titles, credits, and lower thirds. Start from scratch or with one of the animation presets available inside the app. There are countless ways to make your text move with After Effects, from spin to swipe to slide.Combine videos and images to send a UFO across the sky, blur out a logo, or create an explosion — endless possibilities. There are hundreds of effects to get the look you want, from adding fog to changing colors to making it snow.After Effects works seamlessly with other Adobe apps, creates comps, and immediately sees how they look in Premiere Pro CC with Adobe Dynamic Link. Import work from Photoshop, Illustrator, Illustrator, Illustrator, Illustrator, Character Animator, Adobe XD, and Animate CC. Use Team Projects to collaborate with editors no matter where they’re located. And After Effects is integrated with 300+ software and hardware partners.Adobe offers a complete set of animation apps that work with all your ideas — and each other. Create cinematic movie titles, intros, transitions, and more with After Effects CC. Use Animate CC to create interactive vector animations for games, apps, and the web. Animate characters in real-time with Character Animator CC. And move seamlessly between them with the most comprehensive integration out there.Overview of Adobe After Effects CC FeaturesAdvanced puppet tools for mesh sculptingGet depth passes from native 3D elementsSupercharge your animation flowResponsive Design — TimeSystem Requirements and Technical DetailsIntel Core2 Duo or AMD Phenom II processor; 64-bit support requiredMicrosoft Windows 7 with Service Pack 1, Windows 8, and Windows 8.1. See the CS6 FAQ for more information about Windows 8 support.4 GB of RAM (8 GB recommended)3 GB of available hard disk space; additional free space required during installation (cannot install on removable flash storage devices)Additional disk space for disk cache (10 GB recommended)1280 x 900 displayOpenGL 2.0-capable systemDVD-ROM drive for installation from DVD mediaQuickTime 7.6.6 software required for QuickTime featuresOptional: Adobe-certified GPU card for GPU-accelerated ray-traced 3D renderer### 2. **Interface Overview:** - Familiarize yourself with the After Effects interface, which includes panels like Composition, Timeline, Project, and Preview. Understanding the layout will make navigation easier.### 3. **Creating a New Composition:** - Open After Effects and create a new composition by selecting "Composition" > "New Composition" from the menu. Set the dimensions, duration, and other settings.### 4. **Importing Assets:** - Import your media files (footage, images, audio) into the project panel. You can do this by dragging files directly into the project panel or using the "File" > "Import" option.### 5. **Adding Layers:** - Arrange your assets in the timeline to create layers. Right-click in the timeline and select "New" to create new layers, such as text or solid layers.### 6. **Keyframes and Animation:** - After Effects is built on keyframes. Learn how to set keyframes to animate properties over time. You can do this by selecting a property, clicking the stopwatch icon, and adjusting the property at different points in time.### 7. **Effects and Presets:** - Explore the Effects & Presets panel to apply various effects to your layers. Experiment with different effects to enhance your animations.### 8. **Text and Typography:** - After Effects has robust text tools. Learn how to create and animate text layers. Experiment with text animations, tracking, and kerning.### 9. **Masking and Rotoscoping:** - Understand how to use masks to hide or reveal parts of a layer. This is essential for compositing and creating visual effects.### 10. **Working with 3D:** - After Effects has 3D capabilities. Learn how to create and animate 3D layers. This is useful for creating depth and realistic motion.### 11. **Expressions:** - Explore the basics of expressions to create dynamic animations and automate repetitive tasks.### 12. **Rendering and Exporting:** - When you're finished with your composition, learn how to render and export your project. Go to "Composition" > "Add to Render Queue" to set rendering parameters.### 13. **Community and Tutorials:** - Join online communities and forums like the Adobe After Effects subreddit. There are numerous tutorials available online to help you master specific techniques and workflows.### 14. **Practice and Experiment:** - The best way to learn is by doing. Experiment with different features, tools, and effects. Don't be afraid to make mistakes; that's part of the learning process.### 15. **Keyboard Shortcuts:** - Learn some essential keyboard shortcuts to speed up your workflow. After Effects has many shortcuts that can save you time.Remember, After Effects has a learning curve, so be patient and take the time to explore its features. The more you practice, the more comfortable you'll become with creating dynamic motion graphics and visual effects.
More detailsPublished - Wed, 20 Dec 2023

Created by - Anil Chauhan
zbrush 2024
ZBrush has a unique and powerful user interface designed for digital sculpting and 3D modeling. The interface is highly customizable, allowing users to arrange and organize tools according to their preferences. Here's a general overview of the ZBrush user interface:1. **Title Bar:** - Displays the name of the current document or project. - Contains standard window controls (minimize, maximize/restore, close).2. **Top Shelf:** - Houses various menus and buttons, including File, Edit, Tool, and others. - Quick access to frequently used functions.3. **Palette Trays:** - Located on the left and right sides of the interface. - Hold various palettes such as brushes, materials, and tools. - Can be collapsed or expanded for convenience.4. **Canvas:** - The central area where the 3D model is displayed. - You can rotate, zoom, and pan the model using the mouse or tablet.5. **Draw Palette:** - Contains options for drawing and manipulating objects in 3D space.6. **Tool Palette:** - Displays the currently selected tool (3D brush, insert mesh, etc.). - Allows you to select, edit, and manage your tools.7. **Subtool Palette:** - Manages subtools, which are individual components of your model. - Allows for duplicating, deleting, and organizing subtools.8. **Timeline:** - Used for creating animations and morph targets. - Allows you to manipulate time-based actions.9. **Lightbox:** - Provides access to ZBrush projects, tools, and materials. - Can be toggled on and off with the Lightbox button.10. **Status Bar:** - At the bottom of the interface, it displays information about the current tool, brush, and other settings. - Also includes navigation information and quick buttons.11. **Quick Access Buttons:** - Various buttons for commonly used functions, such as saving, undo/redo, and other options.12. **Customizable Menus:** - You can customize menus and create your own custom interface layouts.ZBrush's interface is known for its flexibility and user-friendly design. It's important to explore the various menus and submenus to discover the full range of features available. Additionally, ZBrush provides extensive documentation and tutorials to help users become familiar with its interface and tools.
More detailsPublished - Thu, 21 Dec 2023

Created by - Anil Chauhan
After Effect User Interface
As of my last knowledge update in January 2022, Adobe After Effects has a user interface that is designed for video editing, motion graphics, and visual effects compositing. Keep in mind that software interfaces can be updated, so there may have been changes since then. Here's a general description based on the version available up to my last update:1. **Workspace Panels:** - **Project Panel:** Displays all the assets (footage, images, audio) you import into your project. - **Composition Panel:** Shows the currently selected composition, allowing you to preview and edit your work. - **Timeline Panel:** Where you arrange and edit your layers over time. - **Layer Panel:** Displays detailed information and controls for the selected layer.2. **Toolbar:** - Contains various tools for creating and manipulating elements in your composition, such as the selection tool, hand tool, and various drawing and text tools.3. **Preview Controls:** - Play, pause, and navigate through your composition with these controls. You can also set work area markers for playback.4. **Effect Controls Panel:** - Displays detailed settings for the selected layer or effect, allowing you to customize parameters.5. **Project and Render Queue:** - These panels help you manage your project files and set up rendering options for exporting your final composition.6. **Info Panel:** - Provides information about the position, scale, and color values of the selected layer.7. **Tools Panel:** - Contains a variety of tools for creating and manipulating elements in your composition.8. **Time Controls:** - Allows you to set the time indicator to a specific frame or time, as well as control the playback speed.9. **Preview Panel:** - Displays a real-time preview of your composition.10. **Menu Bar:** - Houses various menus for accessing different features and functions within After Effects.11. **Workspace Switcher:** - Allows you to switch between different preset workspaces, such as Standard, Animation, or Visual Effects.After Effects has a flexible interface that you can customize according to your workflow preferences. You can resize panels, create custom workspaces, and save layouts for different tasks. Remember that newer versions of After Effects may have introduced changes or improvements to the user interface. If you're using a more recent version, it's a good idea to refer to the official Adobe After Effects documentation for the most up-to-date information.
More detailsPublished - Fri, 22 Dec 2023

Created by - Anil Chauhan
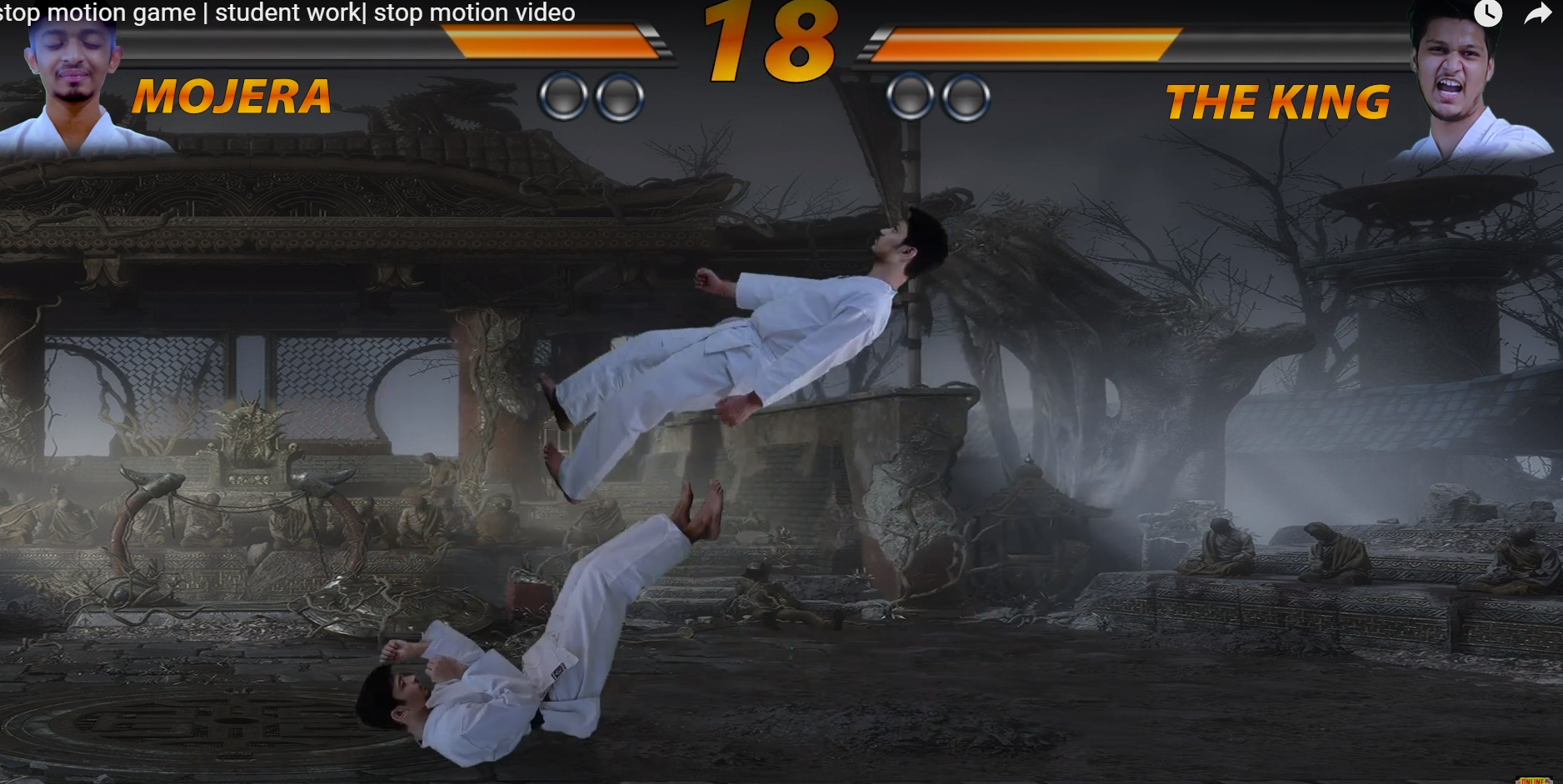
Stop Motion
Stop motion is an animation technique that involves capturing a series of individual frames, each representing a small movement or change, and then playing them in sequence to create the illusion of motion. Unlike traditional animation, where images are drawn or painted, stop motion uses physical objects or puppets that are manipulated frame by frame to achieve movement.https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jp01ddyD4LwHere's a basic overview of how stop motion works:1. **Set Design:** Create a set that serves as the background for your animation. This could be a miniature landscape or a detailed interior, depending on the requirements of your project.2. **Characters and Props:** Design and create characters or objects that will be part of the animation. These can be made from various materials, such as clay (claymation), paper, fabric, or even everyday objects.3. **Frame Capture:** Position your characters or objects on the set and take a photograph. This photograph represents one frame of the animation. Then, move the characters or objects slightly to simulate movement and take another photograph. Repeat this process, capturing many frames.4. **Playback:** When you play back the sequence of frames at a fast speed, the slight movements captured in each frame create the illusion of fluid motion.5. **Editing and Sound:** Once you have captured all the frames, you can edit them together using software. You can add sound effects, music, and dialogue to enhance the final product.Stop motion can be time-consuming and requires patience and attention to detail, but it offers a unique and charming aesthetic. There are various types of stop motion, including claymation (using clay figures), puppet animation (using puppets), and cut-out animation (using flat characters or objects). Famous examples of stop motion animation include films like "The Nightmare Before Christmas" and "Wallace and Gromit."
More detailsPublished - Sat, 23 Dec 2023

Created by - Anil Chauhan
12 Principle in animation
The 12 principles of animation were introduced by Disney animators Frank Thomas and Ollie Johnston in their book "The Illusion of Life." These principles serve as a set of guidelines for creating more realistic and appealing animations. Here's a brief overview of each principle:So what are the 12 Principles of Animation?Squash and stretchAnticipationStagingStraight-ahead action and pose-to-poseFollow through and overlapping actionSlow in and slow outArcSecondary actionTimingExaggerationSolid drawingAppeal1. **Squash and Stretch:** - This principle gives the illusion of weight and volume to characters as they move. Objects or characters should deform slightly when in motion.2. **Anticipation:** - This involves preparing the audience for an action and making the action appear more realistic. It's like a wind-up before the pitch in baseball.3. **Staging:** - Staging is presenting an idea so that it is unmistakably clear. This can involve the placement of characters, use of color, and camera angles to communicate the message effectively.4. **Straight Ahead Action and Pose to Pose:** - "Straight ahead" involves drawing frame by frame from start to end, creating a fluid and dynamic motion. "Pose to pose" involves starting with drawing a few key frames and filling in the intervals later, creating more controlled and refined animations.5. **Follow Through and Overlapping Action:** - Follow through means the termination of an action, and overlapping action is the tendency of parts of the body to move at different rates. Both principles contribute to making movement appear more natural.6. **Slow In and Slow Out:** - The movement of the human body, and most other objects, needs time to accelerate and slow down. This principle helps to achieve a more realistic and fluid motion.7. **Arcs:** - Most actions in life follow an arced trajectory rather than a straight line. Animators use arcs to make movements appear more natural.8. **Secondary Action:** - This is an additional action that reinforces or adds more dimension to the main action. It helps to make the character more realistic and interesting.9. **Timing:** - The number of frames between two poses can affect the speed of an action. Timing is crucial to creating the desired impact and mood in animation.10. **Exaggeration:** - Exaggeration involves taking elements of the animation to the extreme to make the action more exciting and interesting. It should still maintain a sense of believability.11. **Solid Drawing:** - Animators must understand the basics of three-dimensional shapes, weight, balance, light, and shadow to create characters and objects that feel solid and occupy space.12. **Appeal:** - The appeal of a character is crucial for engaging the audience. It involves designing characters in a way that makes them interesting, sympathetic, and memorable.These principles are fundamental to animation and are applicable across various animation styles and techniques. They provide a foundation for creating animations that are visually compelling, emotionally resonant, and believable.
More detailsPublished - Sat, 23 Dec 2023

Created by - Anil Chauhan
Vray Material
VRay (Virtual Reality Ray Tracing) is a popular rendering engine used in various 3D modeling and animation software applications such as 3ds Max, Maya, Rhino, and SketchUp. When working with VRay, creating realistic materials is crucial for achieving high-quality renders. Here's a general guide on creating and working with VRay materials:### 1. **Material Basics:** - In your 3D modeling software, create or select the object you want to apply the material to. - Open the Material Editor and create a new VRay material.### 2. **Diffuse Color:** - Set the base color of the material using the diffuse color parameter. This represents the color of the material under direct lighting.### 3. **Reflection and Refraction:** - Adjust reflection and refraction settings to control how the material interacts with light. This is crucial for achieving realistic surfaces, especially for materials like glass or metal.### 4. **Bump and Normal Maps:** - Use bump maps or normal maps to add surface detail without increasing the geometry complexity. These maps simulate small surface variations, adding realism to the material.### 5. **Specular Highlights:** - Adjust the specular highlights to control the shininess of the material. Higher values result in sharper highlights, while lower values create a more diffuse appearance.### 6. **Transparency:** - For materials like glass or water, adjust the transparency settings. You can control the level of transparency and the color of the material in the transparent state.### 7. **Subsurface Scattering (SSS):** - For materials like skin or wax, consider using subsurface scattering to simulate light penetration beneath the surface, creating a more realistic appearance.### 8. **Displacement:** - Use displacement maps to add detailed geometry to the surface of the object. This can create realistic surface variations like bumps and wrinkles.### 9. **Fresnel Effect:** - Apply the Fresnel effect to control how reflective a material is based on the viewing angle. This helps simulate real-world reflective behavior.### 10. **Environment and Lighting:** - Consider the overall lighting setup and environment. Adjust the HDRI map or other lighting parameters to enhance the material's appearance.### 11. **Material Libraries:** - VRay often comes with pre-built material libraries. Explore these libraries for a quick start and then customize them to suit your scene.### 12. **Testing and Iteration:** - Regularly test your materials in different lighting conditions and camera angles. Make adjustments as needed to achieve the desired look.### 13. **Resources and Tutorials:** - Take advantage of online resources and tutorials. VRay has a large community, and there are many tutorials available for specific materials and effects.Remember that creating realistic materials often involves a combination of these settings, and experimentation is key. Additionally, the specific steps may vary slightly depending on the 3D modeling software you are using along with VRay.
More detailsPublished - Tue, 26 Dec 2023
Search
Popular categories
Adobe After Effects 2025
28Unreal Engine
14zbrush
10Maya Animation
8zbrush tutorial jewelry
7Maya 2025
5Latest blogs

Advanced Editing Techniques
8 Hours Ago

Introduction to Level Design Through Blocking in Unreal Engine
1 Day Ago

Nuke, animating parameters
1 Day Ago
Write a public review